Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cs) on the coastal seafloor near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant inferred from radiocesium distributions in long cores
Cs) on the coastal seafloor near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant inferred from radiocesium distributions in long coresNakanishi, Takahiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Misono, Toshiharu; Shiribiki, Takehiko; Urabe, Yoshimi*; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Coastal Research, 116(SI), p.161 - 165, 2024/01
Continuous data of Cs-137 concentration in surface seabed sediment around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) from 2012 to 2022 was compiled and its temporal change was fitted by exponential function. In general, Cs-137 concentrations were gradually declining with time. However, at some monitoring points in shallow region, long half-lives and/or large deviations of Cs-137 concentrations were noticed. To gain insight into cesium dynamics in shallow seafloor, long sediment cores were collected at shallow region near the FDNPP, and the vertical profiles of Cs-137 concentration and particle size distribution were determined. At the beach, Cs-137 concentration and particle size distribution were very homogenized from several tens of cm to more than 1 m deep, probably due to strong vertical mixing by wind waves and tides. Therefore, beach sediments have significant Cs-137 reserves in deeper layers at present. It was suggested that the Cs-137 supply from deep layers as well as the land area might suppress the decline of surface Cs-137 concentration in this area. At sampling points located at the bases of cliffs and depressions at the offshore zone, the vertical distributions of Cs-137 concentration were highly heterogeneous, showing the particle size dependency. Moreover, Cs-137 profiles obtained at the same point for several years were quite different. Therefore, it might cause the large fluctuation of Cs-137 concentration at surface sediment over time.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Misono, Toshiharu; Shiribiki, Takehiko*
Kaiyo Riko Gakkai-Shi, 27(2), p.37 - 44, 2023/12
This paper summarizes the general situation of marine monitoring conducted after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the experience of development and operation of USVs, and the possibility of applying unmanned vessels as a tool for nuclear disaster prevention in the future. 0.01 Bq/L or less for seawater and 10 Bq/L or less for seabed soil. Operational tests of three USVs have been continuously conducted for use in such environmental radiation monitoring. Development of these UAVs is underway with a view to utilizing them for seawater sampling, direct measurement of the seafloor soil surface layer, and seafloor soil sampling, depending on their performance. It is necessary to promote the development of USVs for future nuclear power plant accidents.
 Sr (
Sr (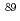 Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areas
Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areasMachida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.119 - 139, 2023/11
We estimate monthly discharged inventory of  Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of
Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of  Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Sato, Hisashi*; Takayama, Yusuke; Suzuki, Hideaki*; Sato, Daisuke*
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-010, 47 Pages, 2023/09
When a high-level radioactive waste repository is constructed in a coastal area, it is necessary to fully evaluate the impact of seawater-based groundwater on engineered barriers, including buffer materials. In this report, one-dimensional saltwater infiltration tests were conducted to obtain data to understand the impact of seawater-based groundwater on the migration phenomena of water and solutes in the buffer material during the transient period. As a result, it was confirmed that the infiltration rate increased as the NaCl concentration in the infiltration solution increased. And it was confirmed that the water content ratio distribution changed as the NaCl concentration in the infiltration solution increased. As a result of analysis of the chloride ion concentration of the post-test specimens confirmed that chloride ion enrichment was occurred with infiltration. As a result of verifying the mechanism by which chloride ion enrichment occurs, it was confirmed that the phenomenon of chloride ion enrichment due to infiltration depends on the initial water content ratio.
Nishino, Saki; Okada, Jumpei; Watanabe, Kazuki; Furuuchi, Yuta; Yokota, Satoru; Yada, Yuji; Kusaka, Shota; Morokado, Shiori; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2023-011, 39 Pages, 2023/06
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) which shifted to decommissioning phase in 2014 had nuclear fuel materials such as the spent fuel sheared powder, the diluted plutonium solution and the uranium solution in a part of the reprocessing main equipment because TRP intended to resume reprocessing operations when it suspended the operations in 2007. Therefore, we have planned to remove these nuclear materials in sequence as Flush-out before beginning the decommissioning, and conducted removal of the spent fuel sheared powder as the first stage. The spent fuel sheared powder that had accumulated in the cell of the Main Plant (MP) as a result of the spent fuel shearing process was recovered from the cell floor, the shearing machine and the distributor between April 2016 and April 2017 as part of maintenance. Removing the recovered spent fuel sheared powder was conducted between June 2022 and September 2022. In this work, the recovered powder was dissolved in nitric acid at the dissolver in a small amount in order to remove it safely and early, and the dissolved solution was sent to the highly radioactive waste storage tanks without separating uranium and plutonium. Then, the dissolved solution transfer route was rinsed with nitric acid and water. Although about 15 years had passed since previous process operations, the removing work was successfully completed without any equipment failure because of the organization of a system that combines veterans experienced the operation with young workers, careful equipment inspections, and worker education and training. Removing this powder was conducted after revising the decommissioning project and obtaining approval from the Nuclear Regulation Authority owing to operating a part of process equipment.
Watanabe, Kazuki; Kimura, Norimichi*; Okada, Jumpei; Furuuchi, Yuta; Kuwana, Hideharu*; Otani, Takehisa; Yokota, Satoru; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2023-010, 29 Pages, 2023/06
The Krypton Recovery Development Facility reached an intended technical target (krypton purity of over 90% and recovery rate of over 90%) by separation and rectification of krypton gas from receiving off-gas produced by the shearing and the dissolution process in the spent fuel reprocessing at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) between 1988 and 2001. In addition, the feasibility of the technology was confirmed through immobilization test with ion-implantation in a small test vessel from 2000 to 2002, using a part of recovered krypton gas. As there were no intentions to use the remaining radioactive krypton gas in the krypton storage cylinders, we planned to release this gas by controlling the release amount from the main stack, and conducted it from February 14 to April 26, 2022. In this work, all the radioactive krypton gas in the cylinders (about 7.1 10
10 GBq) was released at the rate of 50 GBq/min or less lower than the maximum release rate from the main stuck stipulated in safety regulations (3.7
GBq) was released at the rate of 50 GBq/min or less lower than the maximum release rate from the main stuck stipulated in safety regulations (3.7 10
10 GBq/min). Then, the equipment used in the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas and the main process (all systems, including branch pipes connected to the main process) were cleaned with nitrogen gas. Although there were delays due to weather, we were able to complete the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas by the end of April 2022, as originally targeted without any problems such as equipment failure.
GBq/min). Then, the equipment used in the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas and the main process (all systems, including branch pipes connected to the main process) were cleaned with nitrogen gas. Although there were delays due to weather, we were able to complete the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas by the end of April 2022, as originally targeted without any problems such as equipment failure.
Suzuki, Hideaki*; Takayama, Yusuke; Sato, Hisashi*; Watahiki, Takanori*; Sato, Daisuke*
JAEA-Research 2022-013, 41 Pages, 2023/03
It is anticipated that the coupled thermal-hydraulic-mechanical and chemical (THMC) processes will occur, involving an interactive process with radioactive decay heat arising from the vitrified waste, infiltration of groundwater from the host rock into the buffer material, swelling pressure of buffer material due to its saturation and chemical reaction between bentonite and pore-water in the near-field of a geological disposal system for high-level radioactive waste repository. In order to evaluate these phenomena in the near-field, the THMC model has been developed. In this study, For the purpose of evaluating the near-field infiltration behavior in seawater-type groundwater environment, a hydraulic model was set in which the permeability of the buffer material change depending on the salt concentration in the pore-water. In order to evaluate the drying phenomenon of the buffer material due to waste heat, a temperature gradient water transfer model was set in consideration of the dependence of temperature and pore-water saturation. The THMC analysis of the in-situ experiment of engineered barrier system (EBS) experiment at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory was carried out. The validity of the model was then checked through comparison with measured data.
Misono, Toshiharu; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sanada, Yukihisa; Shiribiki, Takehiko; Urabe, Yoshimi*; Tsuruta, Tadahiko
JAEA-Research 2022-010, 134 Pages, 2023/02
An accident occurred at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) in 2011 and a large amount of radioactive materials were deposited around the 1F. Japan Atomic Energy Agency has continued to conduct research on the dynamics of radioactive materials after the accident. This report summarizes the results of the survey conducted in FY 2021 on the status of marine monitoring survey on radioactive substances. Furthermore, a seabed topography and sediments distribution survey was conducted in the coastal area off the Mano River from the Ohta River to understand the topography and sediment distribution. Furthermore, in order to evaluate the inflow of radioactive Cs from the river, the horizontal distribution of the radioactive Cs concentration on the surface sediment in front of the rivers was measured. As basic information on the effects of radioactive materials on marine products, the distribution status of fish was investigated. In addition, a demonstration test of water sampling and sediment sampling was conducted using an unmanned observation vessel. From these results, we estimated the distribution and its dynamics of radioactive Cs in the sediments in the front area on the 1F.
Ikenoue, Tsubasa; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kamidaira, Yuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.61 - 71, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)We conducted numerical simulations on the oceanic dispersion of dissolved radionuclide hypothetically released from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant using long-term oceanographic reanalysis data. We evaluated the characteristics and trends of dissolved radionuclide behavior in the ocean using statistical analysis based on the simulation results. The surface meridional current at the release point in the Fukushima coastal ocean and the Kuroshio Extension significantly affected the north-south transport of the surface radionuclide in the Fukushima coastal ocean and the eastward transport of the offshore surface radionuclide, respectively. Because the surface kinetic energy in the coastal to the offshore area was larger, the range of the dispersed surface radionuclide tended to be larger. In summer (July-September), the increased frequency radionuclide entrainment by the Kuroshio Extension because of the surface southward radionuclide transport in the Fukushima coastal ocean and the large surface kinetic energy caused a large dispersed surface radionuclide. In winter (January-March), the decreased frequency radionuclide entrainment by the Kuroshio Extension because of the surface northward radionuclide transport in the Fukushima coastal ocean and the small surface kinetic energy caused a small dispersed surface radionuclide.
Machida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(1), p.12 - 24, 2023/01
We estimate inventory of tritium in two sea areas corresponding to coastal and offshore ones around Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) based on the measurement results of sea-water tritium concentration monitored constantly from 2013 to Jan. 2021 by using Voronoi tessellation scheme. The obtained results show that the offshore area inventory and its temporal variation amount correspond to approximately 1/5 and 1/40 of that of the treated-water accumulated inside 1F, respectively. These results just suggest that the presence of tritium already included in sea-water as the background is non negligible in evaluating the environmental impact by releasing the accumulated treated-water into the sea region. We also estimate the offshore area inventory before 1F accident and find that it had exceeded over 1F stored inventory over about 30 years from 1960s to 1980s with approximately 4 times larger in the peak decade, 1960s. This fact means that we had already experienced more contaminated situation over 30 years in the past compared to the conservative case appeared by just releasing whole the present 1F inventory. Here, it should be also emphasized that the past contaminated situation was shared by the entire world. We further extend the estimation region into a wider region including an offshore area from Miyagi to Chiba prefectures and find that the area average inventory is now comparable to a half of the present 1F one. Finally, we estimate internal dose per year via ingesting fishes caught inside the area when 1F inventory is just added inside the area and kept for a year. The result indicates that it approximately corresponds to 1.0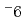 of the dose from natural radiation sources. From these estimation results, it is found that all the tritium inventory stored inside 1F never contribute to significant dose increment even when it is instantly released into the area.
of the dose from natural radiation sources. From these estimation results, it is found that all the tritium inventory stored inside 1F never contribute to significant dose increment even when it is instantly released into the area.
Omori, Kazuki; Yamauchi, Sho; Yanagibashi, Futoshi; Sasaki, Shunichi; Wada, Takuya; Suzuki, Hisanori; Domura, Kazuyuki; Takeuchi, Kenji
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-18-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.245 - 248, 2022/07
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), which is shifted to decommissioning stage, stores large amount of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW). Although TRP is implementing vitrification of HLLW to reduce the risks related to HLLW storage, additional 20 years are required to complete vitrification of HLLW. Therefore, TRP is implementing safety countermeasure related to seismic resistance of HLLW storage facility as one of the top priorities. The results of the seismic evaluation indicate that although the facility itself is seismically resistant, there is a risk of insufficient binding force acting between the facility and the surrounding ground. Thus, replacement of the surrounding ground with concrete is performed. Since the countermeasures, to protect existing buries structure and coordinate with the other construction projects around the site, are required, the dedicated team was setup to handle the process and safety management of the concrete replacement construction.
 O
O -pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawater
-pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawaterMizumachi, Takumi*; Sato, Minami*; Kaneko, Masashi; Takeyama, Tomoyuki*; Tsushima, Satoru*; Takao, Koichiro*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(16), p.6175 - 6181, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.43(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Based on unique 5-fold equatorial coordination of UO
 , water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H
, water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
 in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
 /CO
/CO
 , pH 8), saldian
, pH 8), saldian shows the strongest complexation with UO
shows the strongest complexation with UO
 to form UO
to form UO (saldian) (log
(saldian) (log
 = 28.05
= 28.05  0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
 from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
Machida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 21(1), p.33 - 49, 2022/03
We estimate monthly discharge inventory of tritium from the port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun 2013 to Mar 2020 by using the Voronoi tessellation scheme, following that the tritium monitoring inside the port has started since Jun 2013. As for the missing period from the initial month, Apr 2011 to May 2013, we calculate it by utilizing the concentration ratio of tritium to that of  Cs in stagnant contaminant water during the initial direct discharged period to Jun 2011 and the discharge inventory correlation between tritium and
Cs in stagnant contaminant water during the initial direct discharged period to Jun 2011 and the discharge inventory correlation between tritium and  Cs for the next-unknown continuously-discharged period up to May 2013. From the all- estimated results over 9 years, we find that the monthly discharge inventory sharply dropped just after closing the sea-side impermeable sea-wall in Oct. 2015 and subsequently coincided well with the sum of those of drainage and subdrain. By comparing the estimated results with those in the normal operation period before the accident, we point out that the discharge inventory from 1F port is not so large compared to those during the normal operation. Even the estimated one in year 2011 is found to be comparable to the maximum of operating pressurized water reactors discharging relatively large inventory in the order. In the nation level, the whole Japan domestic discharge inventory significantly decreased after the accident due to operation shutdown of most plants. Furthermore, 1F and even Japanese total discharge inventory are found to be entirely minor when comparing those of nuclear reprocessing plants and heavy-water reactors in world-wide level. From the above, we suggest that various scenarios can be openly discussed on the management in tritium stored inside 1F with help of the present estimated data and its comparison with the past discharge inventory.
Cs for the next-unknown continuously-discharged period up to May 2013. From the all- estimated results over 9 years, we find that the monthly discharge inventory sharply dropped just after closing the sea-side impermeable sea-wall in Oct. 2015 and subsequently coincided well with the sum of those of drainage and subdrain. By comparing the estimated results with those in the normal operation period before the accident, we point out that the discharge inventory from 1F port is not so large compared to those during the normal operation. Even the estimated one in year 2011 is found to be comparable to the maximum of operating pressurized water reactors discharging relatively large inventory in the order. In the nation level, the whole Japan domestic discharge inventory significantly decreased after the accident due to operation shutdown of most plants. Furthermore, 1F and even Japanese total discharge inventory are found to be entirely minor when comparing those of nuclear reprocessing plants and heavy-water reactors in world-wide level. From the above, we suggest that various scenarios can be openly discussed on the management in tritium stored inside 1F with help of the present estimated data and its comparison with the past discharge inventory.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Tetsu To Hagane, 107(12), p.998 - 1003, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In order to clarify the effect of environmental factors on the amount of atmospheric corrosion of steel, novel model for predicting the reduction of atmospheric corrosion considering relative humidity and rain falls was developed. We conducted a one-year calculation simulation of atmospheric corrosion in Miyakojima City, Choshi City, and Tsukuba City using the developed model. Corrosion weight loss by the simulation could reproduce the measured value well. Corrosion weight loss at each point was greatly affected by the amount of flying sea salt, relative humidity, and rain falls.
Otani, Kyohei; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.480 - 486, 2021/12
This is a comprehensive paper of the corrosion of carbon steel in air/solution alternating condition. From cross-sectional observation and analysis of the iron rust layer formed on the surface of carbon steel in the alternating condition, it was found that a multilayered iron rust layer composed of red rust layer ( -FeOOH), rust crust layer (Fe
-FeOOH), rust crust layer (Fe O
O ), inner crystal (Fe
), inner crystal (Fe O
O ), and inner rust layer was formed on carbon steel. The multi-layered iron rust layer would accelerate the cathodic oxygen reduction reaction, and the reason why the corrosion rate of the carbon steel in the alternating condition was accelerated. The effect of artificial seawater (ASW) composition on the corrosion rate of carbon steel in air/solution alternating condition was investigated. It was found that the corrosion rate increased with increasing concentration from pure water to 200 times diluted ASW, and decreased with increasing concentration from 20 times diluted ASW to no diluted ASW. The Mg and Ca ions in ASW precipitated on the reaction interface and formed a metal cation layer, which inhibited the oxygen reduction reaction, and thus the corrosion of carbon steel was inhibited in the highly concentrated ASW.
), and inner rust layer was formed on carbon steel. The multi-layered iron rust layer would accelerate the cathodic oxygen reduction reaction, and the reason why the corrosion rate of the carbon steel in the alternating condition was accelerated. The effect of artificial seawater (ASW) composition on the corrosion rate of carbon steel in air/solution alternating condition was investigated. It was found that the corrosion rate increased with increasing concentration from pure water to 200 times diluted ASW, and decreased with increasing concentration from 20 times diluted ASW to no diluted ASW. The Mg and Ca ions in ASW precipitated on the reaction interface and formed a metal cation layer, which inhibited the oxygen reduction reaction, and thus the corrosion of carbon steel was inhibited in the highly concentrated ASW.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*
Bosei Kanri, 65(10), p.365 - 370, 2021/10
We have developed a new atmospheric simulation model considering important environmental factors such as airborne sea salt, temperature, relative humidity, and rainfall. The developed model was verified by comparing predicted values by the simulation and measured data for the weight loss by atmospheric corrosion. In addition, atmospheric corrosion simulations under open and sheltered exposure condition were conducted, and it was confirmed that the air corrosion weight loss was strongly suppressed by the surface cleaning effect due to rainfall.
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Shiribiki, Takehiko; Misono, Toshiharu; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sanada, Yukihisa; Urabe, Yoshimi*
Journal of Coastal Research, 114(SI), p.320 - 324, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
 I/
I/ I and
I and 
 C records in a modern coral from Rowley Shoals off northwestern Australia reflect the 20th-century human nuclear activities and ocean/atmosphere circulations
C records in a modern coral from Rowley Shoals off northwestern Australia reflect the 20th-century human nuclear activities and ocean/atmosphere circulationsMitsuguchi, Takehiro; Okabe, Nobuaki*; Yokoyama, Yusuke*; Yoneda, Minoru*; Shibata, Yasuyuki*; Fujita, Natsuko; Watanabe, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 235-236, p.106593_1 - 106593_10, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.8(Environmental Sciences)For a contribution to developing the usage of iodine-129 ( I) as a tracer of deep-seated fluid,
I) as a tracer of deep-seated fluid,  I/
I/ I and
I and 
 C were measured for annual bands (AD 1931-1991) of a modern coral collected from Northwestern Australia; the measurements were performed using the JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV for
C were measured for annual bands (AD 1931-1991) of a modern coral collected from Northwestern Australia; the measurements were performed using the JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV for  I/
I/ I and an AMS facility of the University of Tokyo for
I and an AMS facility of the University of Tokyo for 
 C. Results indicate that both
C. Results indicate that both  I/
I/ I and
I and 
 C distinctly increase from 1950s. The
C distinctly increase from 1950s. The 
 C increase can be ascribed to atmospheric nuclear tests, while the
C increase can be ascribed to atmospheric nuclear tests, while the  I/
I/ I increase is due to nuclear-fuel reprocessing as well as atmospheric nuclear tests. These results are in good agreement with previous studies, indicating that the
I increase is due to nuclear-fuel reprocessing as well as atmospheric nuclear tests. These results are in good agreement with previous studies, indicating that the  I/
I/ I measurement by JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV has been further developed.
I measurement by JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV has been further developed.
Takai, Shizuka; Kimura, Hideo*; Uchikoshi, Emiko*; Munakata, Masahiro; Takeda, Seiji
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-007, 174 Pages, 2020/09
The MIG2DF computer code is a computer program that simulates groundwater flow and radionuclide transport in porous media for the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The original version of MIG2DF was released in 1992. The original code employs a two-dimensional (vertical or horizontal cross-section, or an axisymmetric configuration) finite-element method to approximate the governing equations for density-dependent saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and radionuclide transport. Meanwhile, for geological disposal of radioactive wastes, landscape evolution such as uplift and erosion needs to be assessed as a long-term geological and climate events, considering site conditions. In coastal areas, the impact to groundwater flow by change of salinity distribution to sea level change also needs to be considered. To deal with these events in the assessment, we have revised the original version of MIG2DF and developed the external program which enables MIG2DF to consider unsteady landscape evolution. In these developments, this report describes an upgrade of MIG2DF (Version 2) and presents the configuration, equations, methods, and verification. This reports also give the explanation external programs of MIG2DF: PASS-TRAC (the particle tracking code), PASS-PRE (the code for dataset preparation), and PASS-POST (the post-processing visualization system).
Otani, Kyohei; Tsukada, Takashi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(9), p.246 - 252, 2020/09
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of artificial sea water concentration on the corrosion rate of carbon steel under air/solution alternating condition, and to clarify the corrosion mechanism of carbon steel that changes with artificial seawater concentration. Mass measurements showed that the corrosion rate of carbon steel in the alternating condition accelerates with increasing concentration in the concentration region between deionized water to 200 times diluted artificial seawater (ASW), and the corrosion rate decreases with increasing concentration in the concentration region between 20 times diluted ASW to undiluted ASW. It can be considered that the reason why the carbon steel corrosion was suppressed in highly concentrated artificial seawater would Mg ions and Ca ions in the artificial seawater precipitate and cover on the surface due to the increase in pH near the surface by oxygen reduction reaction.